Have you ever questioned how fit you actually are? One of the most effective ways to find out is to calculate your VO2 max. But what exactly is VO2 max, and how do you calculate it at home, with your Apple Watch, or in the lab?
VO2 max, or maximal oxygen uptake, is a measurement of the maximum rate of oxygen your body can consume when exercising. It’s essentially the gold standard for evaluating your cardiovascular fitness and endurance.
Thus, the greater your VO2 max, the more efficiently your body can absorb and utilize oxygen, allowing you to exercise longer and harder before feeling exhausted. Calculating your VO2 max used to require a lab test with various pricey equipment.
However, there are now easier and more accessible methods for evaluating this. You can use the VO2 max formula to calculate your score at home depending on your age, weight, and activity history.
Plus, if you have an Apple Watch, you can measure your VO2 max through the built-in sensors. Many athletes only know about testing for VO2 max in the sports lab but very few know that it can be measured at home or even with a formula. You’ll learn more about calculating your maximal oxygen uptake here.
Table of Contents
What is VO2 Max?
VO2 max refers to the maximum (max) amount (V) of oxygen (O2) your body takes in and utilizes during exercise. Oxygen is critical for your body’s functionality, especially for the respiratory process.
Thus, a higher VO2 max indicates that your body can absorb and utilize oxygen effectively. Your body uses this oxygen to produce the maximum amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) energy required.
In that case, your body can manage aerobic exercises (such as swimming, running, and other cardio) that consume a lot of oxygen.
Also Read: How To Calculate Stride Length By Height
VO2 Max Testing: How To Calculate it
VO2 max testing is usually done in a sports performance lab using a treadmill or stationary bike. The intensity is cautiously calibrated and raised periodically. Before the test, you’ll be required to wear a face mask connected to a machine.
It analyzes your respiratory rate and volume, plus the oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration in inhaled and exhaled air. Again, you’d be outfitted with a heart strap around your chest to measure your heart rate.
It will only take between 10 and 20 minutes to perform the VO2 max test and calculate your score. Meanwhile, here’s what you should do in preparation for the test:
- Do not train or exercise 24 hours before the test.
- Wear comfy workout outfits.
- Refrain from caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and food at least 3 hours before testing.
You attain VO2 max when your oxygen intake remains unchanged notwithstanding an increase in exertion or effort. At this level, you transition from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism.
Henceforth, you can expect your muscles to grow weary, which compels you to discontinue exercising. You can also calculate your VO2 max at home, we’ll show you how in the later part of this article.
What is a Good VO2 Max?
Factors like gender, age, and fitness level can influence your VO2 max number. Therefore, it varies by individual.
Average VO2 Max For Men
The average VO2 max for men varies based on the above factors along with their activity levels. Below is the chart containing averages for men 18-45 years old.
| Activity level | Average VO2 max |
| Sedentary | 35-40 mL/kg/min |
| Active | 42.5-46.4 mL/kg/min |
| Very active | ≤ 85 mL/kg/min |
Average VO2 Max For Women
The average VO2 max for women varies based on the above factors along with their activity levels. Below is the chart containing averages for women 18-45 years old.
| Activity level | Average VO2 max |
| Sedentary | 27-30 mL/kg/min |
| Active | 33.0-36.9 mL/kg/min |
| Very active | ≤ 77 mL/kg/min |
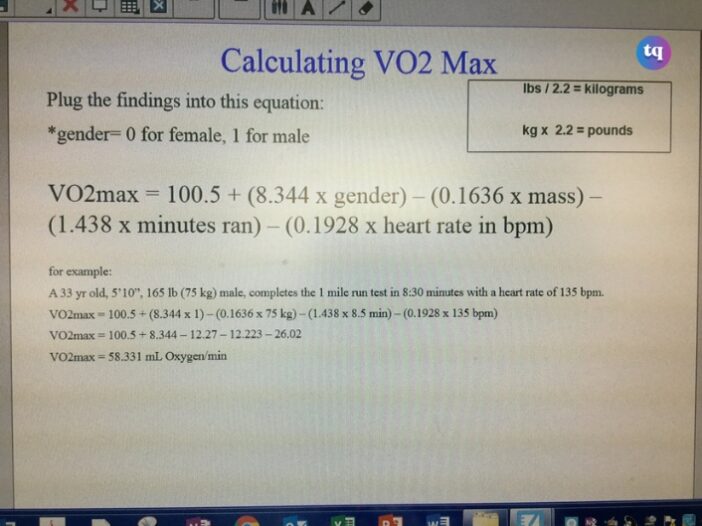
How To Calculate Your VO2 Max at Home
While some athletes might want to perform this test in the sports laboratory, others may not. So depending on your preference, you can either get tested in the lab or calculate your VO2 max at home with a formula or smartwatch (such as an Apple watch).
To measure your VO2 max at home, do the following:
- Use a 1-mile walk test.
- Begin walking as fast as you can but don’t run.
- Now, use a stopwatch to ensure you walk exactly one mile.
- Once you’ve walked one mile, stop the timer immediately.
- Afterward, count your pulse for 15 seconds. Then apply this formula to calculate your VO2 max at home:
VO2 max = 132.853 – (0.0769 x your weight in pounds) – (0.3877 x your age) + (6.315 if you’re male or 0 if you’re female) – (3.2649 x your walking time) – (0.1565 x your heart rate at the end of the test).
Factors Influencing VO2 Max Values
We’ve looked at the average VO2 max scores for men and women in the earlier part of this guide. However, these scores can change over time with training but the following factors can limit these changes:
Age: VO2 max scores normally are highest at age 20 and fall by about 30% by age 65.
Gender: Elite female athletes often have greater VO2 max values than male athletes. However, when values are adjusted for body size, hemoglobin content, and blood volume a man’s VO2 max is typically 20% greater than a woman’s.
Altitude: Since greater altitudes usually have less air for consumption, altitudes significantly impact VO2 max scores. Therefore, an athlete’s VO2 max reduces by 5% for every 5,000 feet gained.
Top VO2 max scores are linked to endurance sports like cycling, cross-country skiing, distance running, and rowing. However, VO2 max scores are not always associated with sports superior performance. Although they can help you to a large extent, factors like nutrition, lactate threshold training, psychological preparation, and skills training may be more important.
FAQs
Use this formula to calculate your VO2 max:
VO2 max = 132.853 – (0.0769 x your weight in pounds) – (0.3877 x your age) + (6.315 if you are male or 0 if you are female) – (3.2649 x your walking time) – (0.1565 x your heart rate at the end of the test).
Maximal exercise tests are performed to determine VO2 max when exercising at your peak effort. These are often conducted in a laboratory or other testing facility. You’ll breathe into a mask while running on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike.
Untrained healthy males typically have a V̇O2 max of 35-40 mL/(kg·min). Whereas, untrained healthy females typically have a V̇O2 max of 27-31 mL/kg·min. These scores can improve with training and decline with age, but the degree of trainability varies greatly.
(W x 11.4, 260 + bodyweight x 3.5)/weight. In the equation, W represents the maximum workload in watts, body weight in kg, and the constant 260 mL.
Working at a high intensity is the most effective way to improve your Vo2 max. Many running coaches advise training at 90-95% of your maximum heart rate. Working at or near your maximum heart rate strengthens your heart’s muscles and increases the amount of blood it can pump per beat.
How To Improve Your Maximal Oxygen Uptake
You should consider improving your maximum oxygen intake if you’re preparing your body to successfully tolerate enough cardio. With a high VO2 max, you can run, swim, or perform other cardio exercises at a greater intensity for a long period.
Additionally, knowing your maximum oxygen uptake is an excellent starting point for assessing your athletic ability if you intend to compete or train at specific levels. But if you don’t have a reasonable VO2 max value or score, these exercises can help you improve it.
- Low-intensity workouts such as rowing, hiking, biking, or running.
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT). This requires performing some minutes of hard aerobic activity, then decreasing intensity for a few minutes before increasing again.
Bottom Line
Understanding how to measure your VO2 max is an effective way to assess your cardiovascular fitness and track your improvement over time. You can use the VO2 max formula, an Apple Watch at home, or visit a sports performance lab to calculate your VO2 max value/score. Knowing this will help you train smarter and challenge yourself to new fitness levels.